As wireless devices become more ubiquitous and advanced in their capabilities, demands on the wireless IP network continue to surge. Fortunately, the wireless network technology advancements are keeping pace with those demands. With 802.11ac, demanding applications such as media streaming that were once relegated to the hardwired network are now achievable wirelessly. We have discussed the 802.11ac standard in previous installments of this column. Now, let’s take a closer look at the technology to better understand how the average home or business user might benefit from these 802.11ac performance enhancements.
How Does 802.11ac Improve Wireless Performance?
802.11ac is the most current and advanced form of the IEEE Wireless Standard. It is designed specifically for the 5GHz band and is backwards compatible with 802.11a and 5GHz 802.11n. It builds on the successful deployment of 802.11n by offering more bandwidth, more MIMO streams, expanded channel bandwidth, and multi-user MIMO.
-
More bandwidth: 5GHz 802.11n offers up to 600Mbps and jumps to 1300Mbps with 802.11ac. More bandwidth means more Internet streams with better gaming, and higher quality video, music, and data streaming.
-
More MIMO streams: The maximum number of steams supported with 802.11n was 4. This number doubles with 802.11ac, which allows more data to be delivered to more client devices at the same time while increasing the number of devices a single AP can support.
-
Expanded channel bandwidth: The maximum allowed channel bandwidth with 802.11n was 40MHz. With 802.11ac, 80MHz is a minimum and up to 160MHz is available, providing significantly more bandwidth for passing data.
-
Multi-user MIMO: This allows for up to 4 simultaneous downloading clients. This advancement provides a better user experience—allowing the kids to play their online games and still deliver enough wireless data throughput for dad to watch Netflix while mom is talking over the VoIP phone.
802.11n Simultaneous vs. 802.11ac Simultaneous
What is MIMO and What Does it Mean to My Wireless Network?
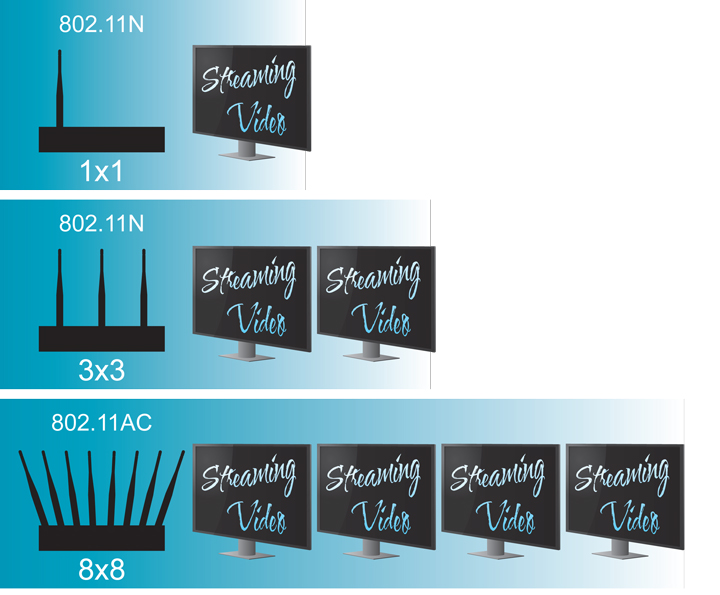
MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) refers to the ability of a wireless device to transmit (Tx) and/or receive (Rx) multiple data streams at once. Earlier Wi-Fi versions (i.e. 802.11 a/b/g) only offered a single transmitter and a single receiver. This is referred to as a 1×1 device because only one Tx/Rx channel is available at a time. With 802.11ac there are more options: 1×1, 2×2, 3×3 and on up to the maximum of 8×8. This is a primary reason we can have more active concurrent connections. MIMO also partially defines the speed the devices can actually attain. As an example, see the table below:

802.11n vs. 802.11ac MIMO Speeds
As the table shows, 802.11ac delivers more data with each added antenna. This also impacts the multi-user MIMO built into the 802.11ac standard—the more Tx/Rx connections available, the more multi-user MIMO connections supported. 802.11ac supports up to 4 simultaneous multi-user MIMO connections, allowing the kids to play video games online, mom and dad to watch an HD movie on Netflix, Uncle Bob to stream his favorite YouTube content and Aunt Patty to listen to her favorite music on Pandora all at the same time—something that would have been impossible with a single AP implementing earlier 802.11 standards.
Will 802.11ac Improve the Performance of All My Devices?
While 802.11ac is significantly faster than previous versions of the 802.11 standard, the end user device must support 802.11ac in order to take full advantage of the connection. 802.11ac runs in the 5GHz range which is much larger and more open than the congested 2.4GHz range used by 802.11b/g/n. An 802.11a/b/g/n device supports 5GHz, but still does not take full advantage of the benefits offered by 802.11ac. An 802.11b/g/n device only supports the 2.4GHz range. The other thing to remember is that the 802.11ac MIMO capability allows for better support of more client devices in general. When selecting client devices, be sure to check for 802.11ac compatibility in order to take full advantage of the 802.11ac wireless network. One thing to also note is that the 802.11ac architecture allows 5GHz 802.11n and 802.11ac devices to coexist without the hit to performance experienced in 802.11g and 802.11n mixed environments.
802.11ac Devices

Luxul’s new 802.11ac 3×3 (AC1900) Access Point, the XAP-1510
With media streaming and other demanding mobile applications becoming such a driving force in our homes, offices and culture, better wireless networking is a necessity. 802.11ac delivers a big step up in terms of wireless network performance. While many client devices are still catching up to this standard, the average home or business owner can benefit immensely from the ability to have more client devices active on the wireless network and improved overall performance for each of those devices. A well-executed 802.11ac solution provides the backbone for a wireless network that is equivalent to that of a wired network—allowing the streaming media performance once enjoyed only by having multiple Ethernet drops throughout the home or office.
